
It's easy to become confused by all the different wine terminology. As you delve more deeply into the world of wine, chances are you'll encounter many industry-specific terms. The definitions below should provide a good basis for understanding terminology associated with wine.
Wine Definitions and Terms
Print the PDF version for a printable copy of the most common wine terminology to use at your next wine tasting. If you need help downloading the printable version, check out these helpful tips.
Created by Inês Saldanha for Love To Know Owned by LoveToKnow. Copyright by LoveTo Know Glossary of Wine Terms thumbnail
A
- ABV (Alcohol by Volume) - A measure of the alcohol concentration of a wine, usually expressed as a percentage.
- Aeration - Adding oxygen to the wine to soften tannins.
- Alcohol - Ethanol; in wine it is produced via fermentation with yeast and sugar.
- Amphora - An Italian clay vessel used for fermenting wine.

Karen Frazier Used with permission Clay amphora for fermenting wine
- AOC (Appellation d'origine contrôlée) - A term in the French wine designation system which means "controlled designation of origin." It determines. It identifies the location or region where a wine is made.
- Appellation - A designated wine growing area governed by specific rules regarding the wine grapes grown and wine produced in the specific appellation areas.
- Aromatized - A wine that has botanicals infused. Vermouth is an aromatized wine.
- AVA (American Viticultural Area) - A designated wine-growing region in the United States.
B
- Barrel - A wooden cask used for fermenting and aging wine.
- Barrique - French oak barrel used for aging and fermenting wine.
- Biodynamic - Farming and winemaking practices that include certain growing techniques and making wines without intervention such as adding yeast.
- Blend - Wine made from more than one type of wine and/or grape.
- Bordeaux blend - A wine made from Bordeaux grape varietals such as Cabernet Sauvignon, Merlot, Cabernet Franc, Petit Verdot, and Malbec, made outside of the Bordeaux region.
- Botrytis - Also called noble rot, botrytis cinera is a fungus that affects wine grapes adding complex and tropical flavor profiles to the finished wines. See also noble rot.

- Bottle age - How long a wine has spent maturing in the bottle.
- Breathing - When wine is decanted, allowing it to react with air.
- Brettanomyces - A wine fault; a type of yeast that can add flavors of barnyard or funk to wine.
- Brix (°Bx) - Sugar levels in wine grapes.
- Blush wine - A pink or rosy wine. See also rosé.
- Brut - A term used in sparkling wine to indicate the wine is very dry.
C
- Carbonic maceration - Winemaking technique where grapes are fermented in the presence of carbon dioxide.
- Chaptalization - Winemaking technique in which sugar is added to a wine during fermentation to increase the final alcohol content.
- Charmant - A method for making sparkling wines in which secondary fermentation is done in a stainless steel tank; also called the "tank method."
- Claret - British term to describe red Bordeaux wines.
- Classified growth - In Left Bank Bordeaux regions, wines are organized in a hierarchy from the highest quality to the lowest. There are five levels of classified growth - First Growth through Fifth Growth. See also cru classé.
- Cooked - A wine that has been exposed to high heat or extreme temperature fluctuations; cooked wines have off flavors and taste of stewed fruit.
- Cork taint - A condition in which a cork infected with fungus taints the wine; wines with cork taint often smell musty or like wet dog. See also TCA.
- Corked - Term describing a wine with cork taint.

- Crianza - A term used on Spanish wine labels. Crianza indicates the wine has spent at least one year in oak barrels.
- Cru - The French word for 'growth'. See also classified growth.
- Cru classé - French term for classified growth.
- Crush - Grape harvest.
- Cuvée - Wine blend. This term is most frequently used in Champagne and sparkling wine.
D
- Decant - Pouring the wine from the bottle to another vessel such as a decanter to remove sediment and aerate the wine.
- Demi-sec - Medium dry.
- Dessert wine - A sweet wine with high residual sugar; it is consumed during or after dessert.
- Designation - A controlled area of wine production that is governed by laws specific to the production of wine in that area.
- DO (Denominación de Origen) - Classification used in Spanish wine.
- DOC (Denominazione di Origine Controllata) - Quality assurance labeling designation used in Italian wine.
- DOCG (Denominazione di Origine Controllata e Garantita) - The highest quality labeling designation for Italian wine.
- DOP (Denominación de Origen Protegida) - Protected denomination of origin; a protected geographical status in Spanish wine.
- Dry - Not sweet.
E
- Eiswein - Wine made with grapes harvested while frozen; the result is a sweet, concentrated wine. See also ice wine.
- En Primeur - The French term for "futures." In the Bordeaux region, consumers can purchase "futures" of wines that are still in the barrel and have not yet been bottled. Consumers typically receive the wines after bottling, approximately 18 months later. See also futures.
- Enology - The study of wines. See also oenology.

- Estate wine - Wines made from grapes grown on the estate where the winemaking facility is located.
F
- Filtration - In winemaking, passing wine through a filter or series of filters to remove particles and polish a wine before bottling.
- Fining - A winemaking process where a substance is added to the wine to clarify or soften it before bottling. Common fining substances include egg whites and gelatin.
- Fortified wine - A wine that has a distilled spirit added. Port, Sherry, and Vermouth are all fortified wines.
- Foudre - A large wooden vat used in winemaking; much larger than a barrel or barrique.
- Futures - In Bordeaux, consumers can purchase "futures" of wines that are still in the barrel and have not yet been bottled. Buyers receive the wines after bottling, approximately 18 months later. See also en primeur.
G
- Grand cru - French term meaning wine of top quality.
- Grand cru classé - Classified growth of top quality; this is a definition used in Burgundy.
- Gran cru - Premium classification for Spanish sparkling wine, Cava.
- Gran Reserva - Spanish wine label term indicating the wine was aged at least five years and a minimum of two years in oak.
H
- Hectare - Metric unit of measure equalling 2.471 acres.
- Hybrid - Grapes that are a cross of two or more species.
I
- Ice wine - Wine made from grapes that are frozen, which concentrates flavors and sugars. See also eiswein.
J
- Jeroboam - Large format wine bottle that holds four standard sized (750 mL) bottles of wine or 3.0 liters for sparkling wine or 6 standard sized bottles or 4.5 liters for non-sparkling wine.
L
- Late Harvest - Late harvest wines are made from grapes that are picked at the end of the wine growing season. Waiting until the end of the season allows the grapes to ripen further, resulting in a higher sugar content. The most common example of late harvest wines are dessert wines.
- Lees - The seeds, stems, and skins of the grape.
- Left Bank - The Bordeaux region is divided into two areas on the left and right bank of the Gironde Estuary. Left Bank Bordeaux appellations include Margaux, Pauillac, Saint-Julien, Saint-Estèphe, Pessac-Léognan, and Haut-Médoc.
M
- Maceration - The part of the winemaking process in which the lees are steeped and interact with the wine must. This process extracts tannins, phenol compounds, and fruit flavors.
- Magnum - A large format bottle that contains 1.5 liters of wine, or two regular (750 mL) sized bottles.

- Malolactic fermentation - The process in winemaking of converting malic acid to lactic acid. The result is a softer, buttery wine.
- Meritage - A term California winemakers use to describe a Bordeaux blend.
- Méthode champenoise - Also called the traditional method, it's how Champagne is made using secondary bottle fermentation. Many sparkling wines are made using the traditional method.
- Microclimate -Small variations in climate throughout a region.
- Must - Freshly crushed grape juice containing the pulp, seeds, skins, and sometimes stems of the grapes.
N
- Négociant - French wine merchant who purchases product such as must, fruit, or wines from growers and bottles them as wines under his own brand.
- New World - A term often used to refer to wines not produced in Europe.
- Noble rot - See botrytis.
- NV/non-vintage - Wine made from grapes harvested from a combination of years and/or a combination of vineyards.
O
- Oenology - The study of wine and wine making. See also enology.
- Off - A wine with flavors or aromas that demonstrate the wine is flawed, damaged, or tainted.
- Off-dry - Containing a trace of sweetness.
- Old World - European wines made from vineyards that were established many years ago.
- Orange wine - White wine grapes processed in the same manner as red wine grapes where the juice is left in contact with the skin and seeds for a time. The resulting wine has an orange tint.
- Oxidation - Wine that has spoiled or gone bad due to exposure to air.
P
- Premier Cru - Translated as "first growth," Premier Cru wines are one of the highest classed growth wine in France, second only to Premier Grand Cru.
- Premier Grand Cru - Premier Grand Cru means "first great growth", these wines are the highest classed growth wines in France.
- Press - Extracting juice from solids.
Q
- Quaffable - Drinkable but not special.
R
- Rating - A critic's score for a wine, usually on a 100-point scale, such as a Wine Spectator rating. May also be called a score.
- Red wine - Wine with a light to deep red color made from black-skinned grapes.
- Reserve - Often indicates a winery's best quality wines.
- Residual sugar - The amount of sugar left in wine after the fermentation process. Measured in grams per liter (g/l).
- Rhône blend - A wine blend made with grapes commonly found in wines from France's Rhône region, including Grenache, Syrah, Mourvedre, and Viognier.
- Right Bank - See also Left Bank. In Bordeaux, regions are either on the left or right bank of the Gironde Estuary. Right Bank regions include Pomerol and Saint-Émilion.
- Rosé - See also blush wine. Wine made from red wine grapes or a blend of red and white wines that has a pink tint to it.
S
- Saignée method - A method of making rosé wines in which wine is bled from the must of a red wine to concentrate the red wine further. The juice bled off is used to make the rosé.
- Sec - Dry, not sweet.
- Secondary fermentation - A second period of fermentation.
- Sediment - Solid material that sinks to the bottom of a bottle of wine; often seen in aged wines.
- Single vineyard - Wine made from grapes that all come from one vineyard.
- Solera - A method for blending and aging certain non-vintage wines such as Sherry involving a grouping of barrels.
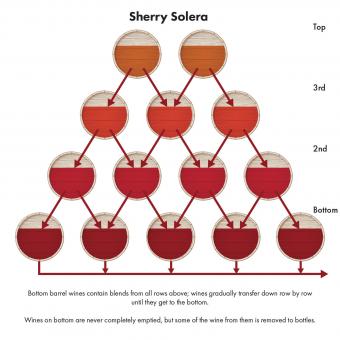
- Sommelier - A sommelier is a person that has extensive wine knowledge through training, classes, and certification.
- Sparkling wine - Any wine with bubbles.
- Split - A single serving bottle of sparkling wine or Champagne, about 187.5 mL.
- Structure - The wine's tannins, acidity, and alcohol content.
T
- Table wine - A wine that is a decent, drinkable wine that isn't premium or expensive.
- Tank - A vat in which wine is aged and fermented.
- Tannins - Tannins are caused by the lees (seeds, stems and skins) of the grape.
- TCA (2,4,6-Trichloroanisole) - The cause of cork taint.
- Terroir - Refers to the soil in which the wine grapes are grown. The terroir imparts its flavors into the wine.
V
- Varietal - The type of grape used in a wine. For example, Chardonnay and Pinot Noir are both varietals.
- Vieilles vignes - A French term that means "old vines".
- Vigneron - A person cultivating wine grapes.
- Vin - French term for wine.
- Vinification - Fermenting grapes into wine.
- Vintage - Refers to the year the grapes were harvested for a particular bottle of wine and not the year the wine was bottled.
- Viticulture - Cultivating grape vines.
- Vitis vinefera - A term used for wine grapes.
W
- White wine - Wine made from bronze skinned grapes.
- Wood aging - Refers to when wine is aged in wood barrels. Wood aging lessens tannin and acid levels, "softening" the wine. The wood of the barrel also contributes flavor characteristics.
Y
- Yield - Amount of grapes produced per vineyard.
Familiarize Yourself With Wine Terminology
These are the basics of wine terminology; there are more associated with wine tasting and a wine's characteristics. It may seem like a lot of wine terminology to remember, but as you use and hear them more and more often, they become easier to remember. You may find that as you expand your wine terminology knowledge, you will also expand your overall enjoyment of wine.







